
- #Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac how to#
- #Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac install#
- #Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac update#
- #Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac full#
- #Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac software#
#Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac how to#
To test out your new user, log out by typing:Īnd log back in with this command in terminal: ConclusionĪfter completing this tutorial, you should have a sense of how to add new users and grant them a variety of permissions in a MySQL database. Just as you can delete databases with DROP, you can use DROP to delete a user altogether: You can review a user’s current permissions by running the following:
Note that when revoking permissions, the syntax requires that you use FROM, instead of TO as we used when granting permissions. If you need to revoke a permission, the structure is almost identical to granting it: Firefox browser for mac.
#Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac update#
If you want to give them access to any database or to any table, make sure to put an asterisk (*) in the place of the database name or table name.Įach time you update or change a permission be sure to use the Flush Privileges command. To provide a specific user with a permission, you can use this framework:
#Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac full#

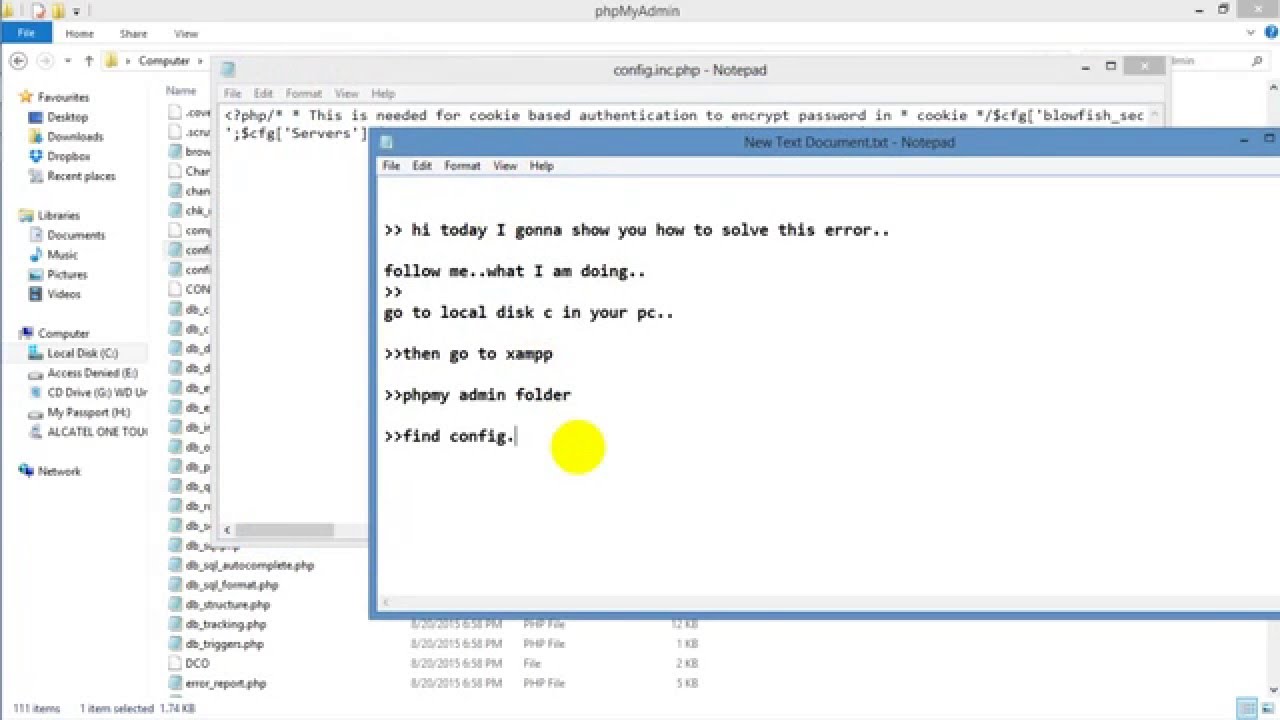
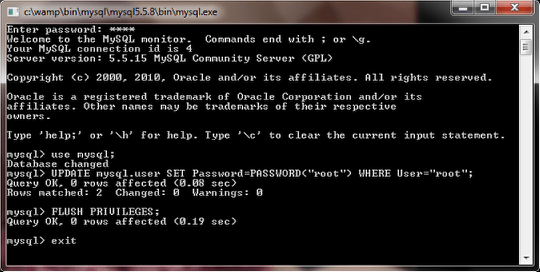
localhost is a hostname which means “this computer,” and MySQL treats this particular hostname specially: when a user with that host logs into MySQL it will attempt to connect to the local server by using a Unix socket file. Note: When adding users within the MySQL shell in this tutorial, we will specify the user’s host as localhost and not the server’s IP address. Let’s start by making a new user within the MySQL shell: However, in cases where more restrictions may be required, there are ways to create users with custom permissions. In Part 1 of the MySQL Tutorial, we did all of the editing in MySQL as the root user, with full access to all of the databases. Throughout this tutorial, any lines that the user needs to enter or customize will be highlighted! The rest should mostly be copy-and-pastable. Once started the service and when I tried connecting to the database, I got the below error: # mysql -u root ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user (using password: NO) MySQL version is as below. I Installed MySQL server (MariaDB 8.0) on my CentOS 7 using yum. For some reason when I installed MySQL on my machine (a Mac running OS X 10.9) the 'root' MySQL account got messed up and I don't have access to it, but I do have access to the standard MySQL account ' ' which I use to log into phpMyAdmin. MySQL: Access denied for user ' ' (using password:NO). Update: as Bozho suggested, I did the following. Access denied for user ' ' (using password:NO) After this I try: mysql -u root -p However, it asks for a password which I don't have.
#Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac install#
I'm trying to login into fresh install mysql with: sudo /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql -u root But getting following error: ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user (using passw. It has a variety of options to grant specific users nuanced permissions within the tables and databases-this tutorial will give a short overview of a few of the many options.
#Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' on mac software#
MySQL is an open-source database management software that helps users store, organize, and later retrieve data. Error 1045 Mysql 28000 Access Denied For User Mac.Mysql Access Denied For User Root Localhost Mac.Mysql Access Denied For User Root Localhost Macos.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
